The dog’s anus is surrounded by glands known as the anal sacs. The fluids produced by these glands are normally secreted during the formation of feces. The fluids are often straw-colored with brown flecks and have a pungent stench. Among the many problems that can occur with anal sacs are inflammatory reaction, infection, blockage, rupture, and malignancies.
Additionally, cancers that start in the anal sacs can move to the abdominal lymph nodes. One or both of the glands may be removed to treat severe or persistent anal gland disorders. But how do you go about it? What steps are involved in removing the damaged anal gland? And what does having a Dog Anus Gland Removal cost? Continue reading with Dogplus24h.com to know more:
Using a laser during one of the procedures to remove anal glands dramatically lessens the amount of bleeding that occurs and expedites the removal of the glands. Other procedures include traditional open surgery, which is currently not regarded as the best choice.
The estimated Dog Anus Gland Removal cost is expected to be between $1,200 to $2,200 because it is a delicate treatment that can only be performed by a veterinarian. Depending on how difficult the extraction is and how long your pet needs to stay in the hospital, the Dog Anus Gland Removal cost will be altered.
What is an anal sacculectomy?
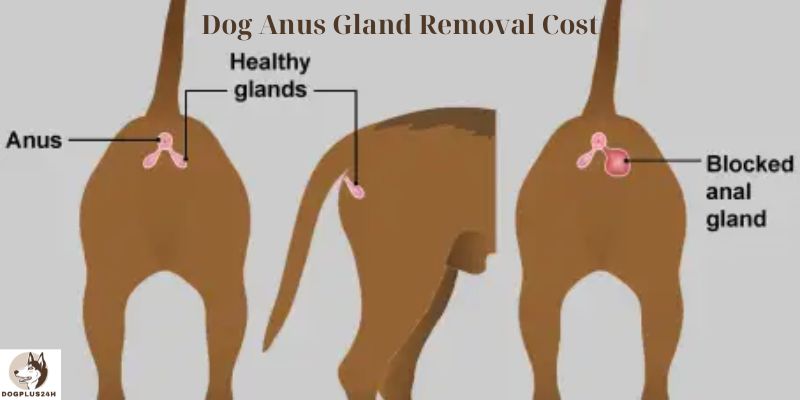
Anal sacculectomy is the medical term for the surgical removal of a dog’s anal glands. In order to indicate its territory, a dog’s anal glands become active when it excretes or performs excrement. When a dog excretes, the main muscles in its lower digestive tract contract, causing the anal glands to release their contents, which is a dense, foul-smelling substance that is particular to every dog.
On the other hand, dogs with anal gland obstruction, inflammation, or edema are unable to expel this substance and frequently need a veterinarian’s help. The veterinarian will need to remove the anal sacs if these problems can’t be resolved with medication.
How can you determine if your pup’s anal glands are having problems?
Watch out for the following red flags:
1. Follow your tail:
Many dogs may chase after their tails in an effort to get to an irritating area, like in the case of an anal sacs problem. It should be remembered that tail-chasing can also be a problem behavior.
2. Scooting:
Your pet will do this activity by sitting on its butt and dragging its rear along the ground. (one of the primary indicators of dog anal gland expression or blockage)
3. Yell out:
This may occur if you go to touch your dog’s tail or anus and they cry out in agony or distress, if you pat them from behind, or you may occasionally detect it while your pet is defecating. You might also experience it if you touch your dog’s hind paw.
4. Excessive Liking:
Your dog may even wind up leaving licking streaks that darken the fur and hair surrounding the affected area as a result of constant licking of the dog’s anus. However, in breeds with darker hair, it could be difficult to tell. If you think your dog is displaying any of the symptoms listed above, schedule a visit with your pet veterinarian right away for a thorough examination.
How to remove the anal sac glands?

The patient (dog) will be unconscious throughout the entire operation. Anal sacculectomy refers to the surgical removal of the anal gland. In order to drain (remove anal gland secretions), both anal sacs must first be manually expressed. After that, a polymer is injected through the duct into the anal glands, where it hardens into a rubbery form upon contact with the glands.
Two incisions are made above the anal glands after the skin around the anus is prepared in this anal gland surgery. The external and internal anal sphincters, as well as the anal gland, are closely connected. To get it out of the sphincter muscles, a very delicate dissection is required. The gland is then removed after the duct has been shut off to prevent any leakage into the tissues nearby from the large intestine or colon. The skin incision is then stitched shut. Your animal friend will then get an immediate injection of painkillers and antibiotics.
The overall Dog Anus Gland Removal cost of the procedure, which can range from $1,600 to $2,100 depending on the patient’s weight, includes the required pre- and post-surgical tests as well as intraoperative and postoperative medications.
- Important Reminder
Please keep in mind that the aforementioned fee DOES NOT INCLUDE any additional postoperative exams or medications as they are typically not required unless the postoperative instructions are ignored.
Dog Anus Gland Removal Cost
Anal sacculectomy is a sensitive technique that can only be carried out by a veterinary surgeon, thus you may anticipate paying between $1,000 and $2,000 for this procedure. Depending on how difficult the removal is and how long your pet needs to stay in the hospital, the Dog Anus Gland Removal cost will change.
What Can You Expect Following Anal Gland Removal?
You will need to give your dog antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs after the procedure. To keep him from licking the wound as it heals, your puppy will also need to wear an electric collar. The purpose of your dog’s anal glands is to scent-mark its territory. Being a household pet, your dog won’t suffer any harm from having the glands removed. Dogs will utilize their poop to mark their territory, much like humans do.
Dogs’ Anal Sacculectomy Recovery
The primary objective of a dog’s post-anal sacculectomy aftercare is pain treatment, along with infection control. The veterinarian will advise painkillers and an antibiotic that must be administered according to instructions. A dog may develop constipation following surgery; however, if after three to four days no stool has been passed, consult your veterinarian.
There will be a need to gently clean the area because other dogs will get diarrhea. Over the course of the first several days, some dogs may require more frequent bowel movements than usual. Take your dog outside more frequently during the first several days following the sacculectomy, regardless of the circumstance.
It is crucial for pet owners to regularly check the incision site for infection because the incision made during surgery is directly related to the rectum. Discharge, discomfort, redness, and swelling are indications of incision site infection and need to be reported to the doctor.
Issues that could arise

After having the anal sac removed, problems may occasionally occur. Some of the immediate effects of an anal sac removal include infection, swelling, scooting, skin irritation, and leakage from the surgical site. The establishment of a stricture, a fistula, and fecal incontinence are all possible long-term effects (abnormal narrowing). A fistula is an irregular tube that connects the surgical site to the underlying tissue. After practically any kind of surgery, fistulas can develop.
Recurrent diseases that discharge are typically brought on by insufficient excision of the anal sac or the duct leading from it. A second procedure might be necessary to remove the leftover tissues. Fecal incontinence may result from removal-related injury to the anal muscles and/or nerves in the anal sac region. The majority of patients fully recover in 10–12 days, and the outlook for their long-term health is often very favorable.
Does the expression of the anal glands harm dogs?
The procedure is typically unpleasant for the dog, and most dogs will cry as soon as you get close to the region around their anal sacs. The good news is that it won’t last much longer. Your veterinarian will be able to speak for you if your dog’s glands get blocked or do not drain regularly. In order to do this, gentle pressure is applied to the glands on either side of the anus in order to force the fluid inside of the gland to release. Additionally, confirm with your veterinarian the successful removal of affected glands.
Are there any obvious sutures left behind after an anal sac has been removed?
Veterinarians typically bury the skin sutures after removing the anal sac. This will guarantee that there won’t be any visible stitches left over after the treatment. Additionally, the hidden sutures will eventually come out on their own. Since it is unnecessary to remove them, they don’t need to be.
Canine Anal Sacculectomy Prevention
Impaction, infection, and abscess are examples of chronic anal disorders that can develop for a variety of reasons. According to experts, the function of a dog’s anal glands is to mark territory and deter predators when they are in danger. Some canines do not properly express the glands, which causes them to overproduce over time.
This issue frequently affects overweight dogs; consult your vet about a weight loss plan for your pet. Even though they had no issues in the past, the glands may now be problematic in dogs who have developed gastrointestinal conditions that impact the consistency of their stools. With the intention of testing whether a thicker food will help the anal sac expulsion process, talk to your dog’s veterinarian about changing its diet.
By having their anal glands expressed as needed by a qualified veterinarian or technician, canines have been prevented from developing problems. This operation, a manual expression of the anal glands that is often performed every few months, if performed improperly, could result in anal gland issues. Pet owners should never let anyone other than a physician express their dog’s anal glands. Unless they have undergone specific training, dog groomers, pet store employees, and dog trainers are often not certified or medically trained to express anal glands in any creature.
Conclusion
Many dog owners claim that when their dog’s glands are not secreted, they swell and feel unpleasant. The dog licked their own anus as a result, which could trigger an infection there. They chose to have the glands surgically removed, Dog Anus Gland Removal cost between $1200 and $2200, in order to avoid that nuisance. The vast majority of dog owners claimed that throughout the procedure, their canine friends showed no signs of discomfort or issues related to the anesthesia’s administration.


